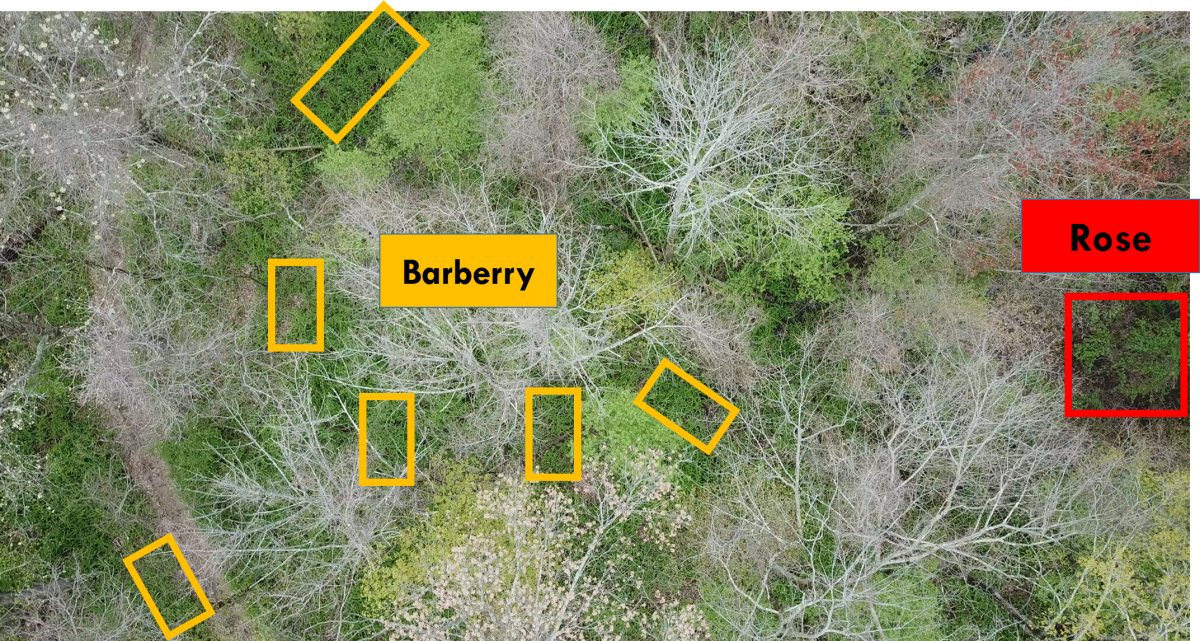
Invasion by non-native plant species is a primary concern in forest ecosystem health and biodiversity. Despite extensive research on invasive species, fundamental questions remain on how to quantify the distribution of their populations accurately. Remotely sensed imagery at low altitudes during distinct phenological states can detect the spatial organization of understory invasive shrub species (fig. 1). This work presents a method of classification of two invasive non-native shrub species, Japanese barberry (Berberis thunbergii) and multiflora rose (Rosa multiflora), using convolutional neural networks (CNN). All aerial imagery was captured at low altitude (40-50 m) over deciduous forest canopies during late March and early May in northeast Connecticut, USA.
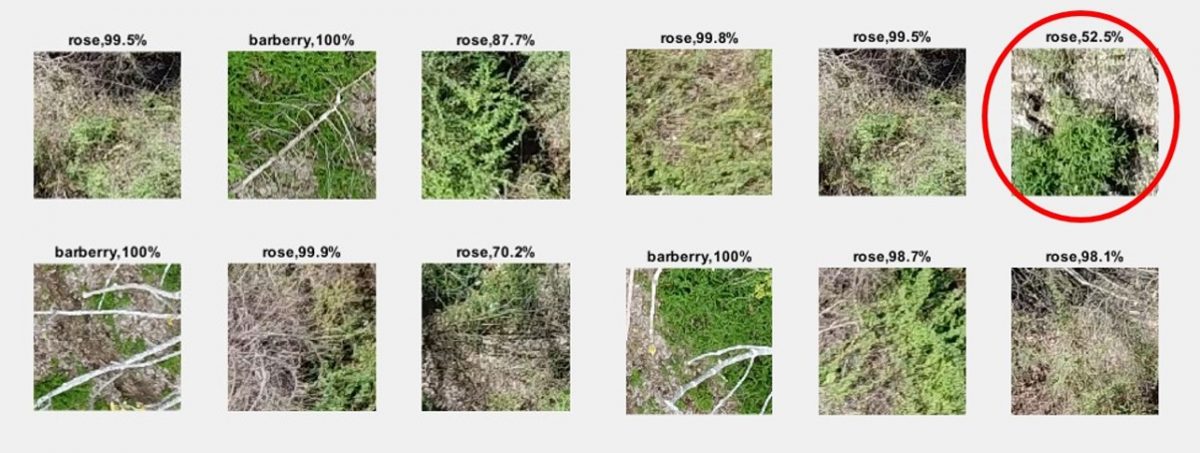
We chose three pre-trained CNN models – Deeplab v3+, U-Net, and RefineNet – as benchmarks for the project. The training dataset consisted of 1855 images, resized to 224 x 224 pixels. Seventy percent of the samples were selected as the training dataset and thirty percent as a validation set. The models achieved an average accuracy of 91 %, 92 %, and 95 %, respectively (fig. 2). This dataset is the first public image dataset of two widespread understory invasive shrub species from New England.
Once the validation process is complete, the resulting plug-in could be used in any mapping software program. The final invasive species occurrence map will allow natural resource professionals to monitor and subsequently manage invasive plants more effectively.
